LDA Topic Modeling: An Explanation
Background
Topic modeling is the process of identifying topics in a set of documents. This can be useful for search engines, customer service automation, and any other instance where knowing the topics of documents is important. There are multiple methods of going about doing this, but here I will explain one: Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA).
The Algorithm
LDA is a form of unsupervised learning that views documents as bags of words (ie order does not matter). LDA works by first making a key assumption: the way a document was generated was by picking a set of topics and then for each topic picking a set of words. Now you may be asking “ok so how does it find topics?” Well the answer is simple: it reverse engineers this process. To do this it does the following for each document m:
- Assume there are k topics across all of the documents
- Distribute these k topics across document m (this distribution is known as α and can be symmetric or asymmetric, more on this later) by assigning each word a topic.
- For each word w in document m, assume its topic is wrong but every other word is assigned the correct topic.
- Probabilistically assign word w a topic based on two things:
– what topics are in document m
– how many times word w has been assigned a particular topic across all of the documents (this distribution is called β, more on this later) - Repeat this process a number of times for each document and you’re done!
The Model
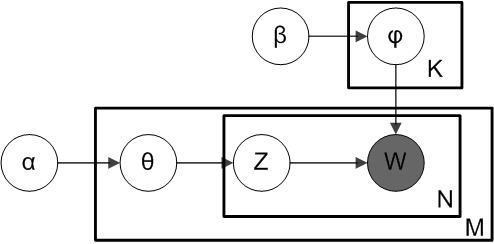
Above is what is known as a plate diagram of an LDA model where:
α is the per-document topic distributions,
β is the per-topic word distribution,
θ is the topic distribution for document m,
φ is the word distribution for topic k,
z is the topic for the n-th word in document m, and
w is the specific word
Tweaking the Model
In the plate model diagram above, you can see that w is grayed out. This is because it is the only observable variable in the system while the others are latent. Because of this, to tweak the model there are a few things you can mess with and below I focus on two.
α is a matrix where each row is a document and each column represents a topic. A value in row i and column j represents how likely document icontains topic j. A symmetric distribution would mean that each topic is evenly distributed throughout the document while an asymmetric distribution favors certain topics over others. This affects the starting point of the model and can be used when you have a rough idea of how the topics are distributed to improve results.
β is a matrix where each row represents a topic and each column represents a word. A value in row i and column j represents how likely that topic icontains word j. Usually each word is distributed evenly throughout the topic such that no topic is biased towards certain words. This can be exploited though in order to bias certain topics to favor certain words. For example if you know you have a topic about Apple products it can be helpful to bias words like “iphone” and “ipad” for one of the topics in order to push the model towards finding that particular topic.
Conclusion
This article is not meant to be a full-blown LDA tutorial, but rather to give an overview of how LDA models work and how to use them. There are many implementations out there such as Gensim that are easy to use and very effective. A good tutorial on using the Gensim library for LDA modeling can be found here.
Have any thoughts or find something I missed? Let me know!
Happy topic modeling!